"The GDPR revolutionises the requirements for the protection of personal data. It requires the use of state-of-the-art solutions. Minimise the risks of processing personal data in web applications with Akamai's security services" – Dr Anna Schmits, EMEA Data Protection Officer, Akamai
GDPR: What is it about?
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is the new EU regulation on data protection that replaces the existing Data Protection Directive 95/46/EC and the multitude of local data protection laws in EU Member States. The GDPR serves to unify data protection laws in Europe and aims to provide comprehensive protection of EU citizens' personal data.
Non-compliance with the regulations of the GDPR, e.g. due to insufficient protection of personal data, can have significant financial consequences and also serious consequences for the respective leaders. Ultimately, the reputation of the company is at stake.
The GDPR is directly applicable in all EU member states and comes into force on 25 May 2018. With regard to data security, the GDPR requires that data processing companies take "appropriate technical and organisational measures" to prevent a data breach from leading to a violation of the rights and freedoms of the EU citizens concerned. Whether a measure is appropriate depends, among other things, on the categories of personal data and the type of processing and requires a risk analysis. The appropriate measures must already be taken before the Directive enters into force in May 2018. Given the large amount of personal and confidential data processed via internet websites and web applications, this is no easy task.
Furthermore, under the GDPR, data processing companies must prove that the measures were appropriate to protect the personal data effectively and efficiently. Often, this proof is made more difficult by the fact that companies use third-party providers for individual data processing processes. Thus, it is necessary to prove that the third-party providers protect the data effectively and efficiently. Even in the case of a large number of processing third parties, the original company remains responsible for the protection of personal data and must provide this proof for each third party. With regard to the principle of accountability under the GDPR, it is therefore absolutely necessary that the controller and/or the third-party providers have taken appropriate technical and organisational measures and – especially in the case of a data breach – are also able to prove that these measures were appropriate.
G&L + Akamai support you in complying with the GDPR
The GDPR requires documented evidence that personal data processed by an organisation is adequately and sufficiently protected. In today's connected world, where many web applications and websites contain or access personal data, this can be a major challenge – not only in terms of the processes and technology used, but also in terms of the specialists required. With the Akamai Intelligent Platform, you can overcome this challenge:
Akamai offers a robust security strategy for web applications, outstanding security experts, flexible processes and state-of-the-art technology. In the following, we would like to give you four recommendations on how you can meet the security requirements for your web applications in accordance with the GDPR:
1) Implement appropriate technical and organisational measures
Large amounts of personal data are processed via web applications. According to the GDPR, companies and organisations must implement appropriate technical and organisational measures to adequately protect the personal data they process in web applications. Such measures should include security technologies for web applications and websites that aim to protect against unauthorised access to personal data – based on risk and best practice.
The Akamai Web Application Firewall (WAF) combines industry best practices (including Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP)) with intelligent assessment mechanisms to identify web attacks. In addition, Akamai security experts continuously monitor the internet for new attacks.
The Akamai WAF is a service that provides risk-based protection against web threats. It is based on the classification of accesses to web applications into risk groups, i.e. risks from highly specialised attacks can be mitigated immediately, effectively and efficiently.
An implementation of the Akamai WAF can thus serve as proof that you, as a customer, have taken all appropriate measures for your web applications to be armed against known and unknown threats from the web.
The web content routed via the Akamai Intelligent Platform is increasingly API-based. The fact that APIs are not sufficiently protected is also explicitly discussed by OWASP (Open Web Application Security Project, www.owasp.org) as an increasing risk that requires special attention. Akamai Kona Site Defender is specifically designed to protect API communication.
Akamai's Kona Site Defender service offers the following benefits:
- Protection of RESTful APIs and XML-based web services
- Minimising the impact of DDoS attacks (bandwidth saturation due to excessive data rates, slow post attacks)
- Data theft (parameter misuse, MITM attacks, injection attacks)
- Provision of the service as a scaled cloud solution to meet the requirements of even the largest companies
- Automated analysis and reporting
- SIEM integration
2) Meet the burden of proof
In the event of a personal data breach, this must be reported to the data protection authority. It is important to be able to provide the DPA with evidence of web attack mitigation measures already in place and those planned for the future to ensure that the impact of these attacks is minimised.
Web application security measures need to be continuously reviewed in light of new and changing web threats to ensure they remain effective. Akamai Security Optimisation Assistance helps organisations respond to the ever-changing threat landscape. The Akamai solution can provide evidence that risks from unauthorised access to personal data in web applications have been actively anticipated and mitigated through the creation and maintenance of effective WAF rules. As part of its services, Akamai provides comprehensive reports and assessments of web attacks, including type, volume and likelihood, always over a defined period of time. As part of the Akamai Managed Kona Site Defender service, an Akamai security expert proactively reviews existing security policies and provides recommendations for ongoing adjustments to WAF rules in light of current web threats.
3) Use of "state of the art" technology
The GDPR requires the use of state-of-the-art3 solutions. With Akamai, you minimise the risks when processing personal data in web applications. This is primarily about securing your web applications against DDoS and application layer attacks.
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks – in conjunction with application layer attack vectors such as SQLInjection (SQLi), Local File Inclusion (LFI), Remote File Inclusion (RFI) and Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) – are an extremely dangerous combination when it comes to the protection breach and exposure of personal data in web applications.
Often, separate web application protection solutions from different vendors are deployed in the customer's (cloud) data centre and are not integrated with each other. This approach delays an effective and rapid response to an acute threat.
"Während Ihre Techniker und Anwendungen damit beschäftigt sind einen DDoS-Angriff abzuwehren, der die Verfügbarkeit Ihrer Services einschränkt, besteht die Gefahr, dass gleichzeitig durch einen verdeckten Angriff auf personenbezogene Daten zugegriffen wird. Akamai kann personenbezogene Daten in Webanwendungen effektiv schützen und auf harmonisierte und koordinierte Weise Schutz vor DDoS- und Application Layer-Angriffen bieten" - Gerhard Giese, Manager Enterprise Security Architects EMEA, Akamai
"While your engineers and applications are busy fending off a DDoS attack that limits the availability of your services, there is a risk that personal data is being accessed at the same time through a covert attack. Akamai can effectively protect personal data in web applications and provide protection against DDoS and application layer attacks in a harmonised and coordinated manner" - Gerhard Giese, Manager Enterprise Security Architects EMEA, Akamai
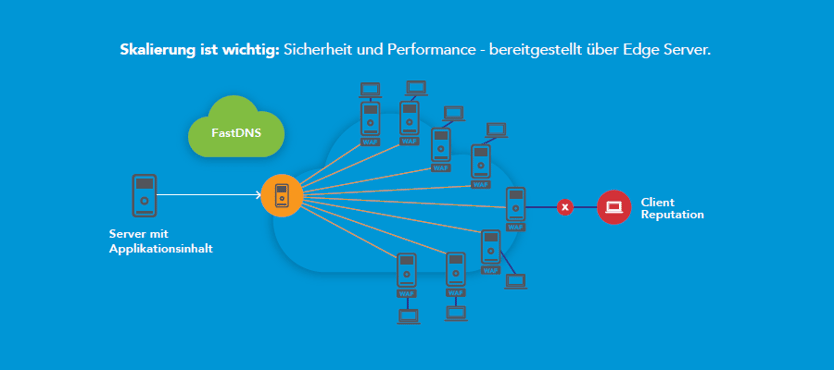 Scaling matters: security and performance – delivered via Akamai Edge ServerScaling matters: security and performance – delivered via Edge Server
Scaling matters: security and performance – delivered via Akamai Edge ServerScaling matters: security and performance – delivered via Edge Server
Because the Akamai Web Application Firewall is part of the Akamai Intelligent Platform, it always delivers customer content via the edge server geographically closest to the user. The WAF is therefore part of the central infrastructure of Akamai's Content Delivery Network. The Akamai Intelligent Platform consists of a global network of over 230,000 servers deployed in more than 1,600 networks in over 130 countries. This network enables attacks to be stopped locally as soon as an attempt is made to attack corporate websites or web applications via the Akamai server – and not only when the attack has already reached your web server in the data centre. This is because it is then very costly to detect the attack, mitigate it and absorb the loads. For this, expensive and normally (if no attack is carried out) oversized equipment would have to be purchased and managed or hybrid solutions would have to be implemented. Akamai's WAF, on the other hand, is installed on thousands of edge servers and easily absorbs the entire load. DDoS attacks, even at the application level, are stopped immediately at the Akamai edge server.
Each customer's WAF rules are quickly applied across thousands of relevant edge servers, protecting your web resources worldwide. Akamai is thus uniquely positioned to protect the entire processing and transmission chain for personal data in web applications – for any type of business and for any web presence.
The effectiveness of Akamai's web application firewall can be further enhanced by reputation checking IP addresses accessing your web applications. Akamai's Client Reputation database captures 1 billion IP addresses each quarter. A small percentage of these addresses are considered dangerous and are ranked on a scale of 1 to 10. These IP addresses can be blocked by the client using WAF rules. Every day, hundreds of millions of IP addresses are analysed for malicious activity. This procedure leads to measurable effectiveness, in most cases with an accuracy of over 95 percent. Evaluating the effectiveness of the implemented protection measures is an important part of the compliance process under the GDPR.
Theft of credentials (username and password) can easily lead to the loss of sensitive personal data. Following a recent disclosure of passwords on the internet, research found that 8.8% of these credentials used one of the seven extremely simple passwords, e.g. "123456" or "password". Many users use simple passwords that they can easily remember. Passwords are also frequently reused. If login data has fallen victim to a hacker attack, it is quite possible that other data sources will also become accessible to the hackers because these data sources are protected with the same password. Attackers use specialised botnets to automatically attack websites and data sources on a global basis with the stolen credentials.
Akamai can minimise these risks. When Akamai Bot Manager Premier is enabled on Akamai Edge servers, all requests to your web resources are scanned and blocked if the IP address has a bad reputation.
4) Implement a zero-trust security strategy
In order for your employees and suppliers to complete their tasks, you need to allow them access to your internal network applications. However, such access for both internal and external people means increased risk to the security of personal data in the web applications and to the network in general. Introducing a zero-trust security strategy effectively supports you in complying with the GDPR requirements.
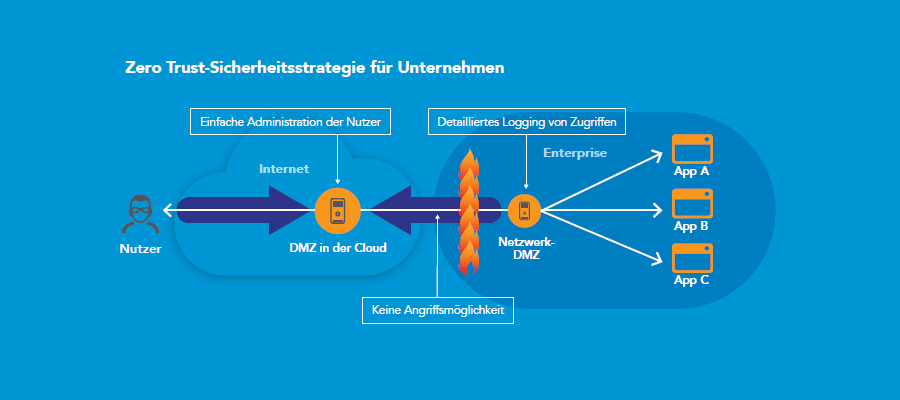
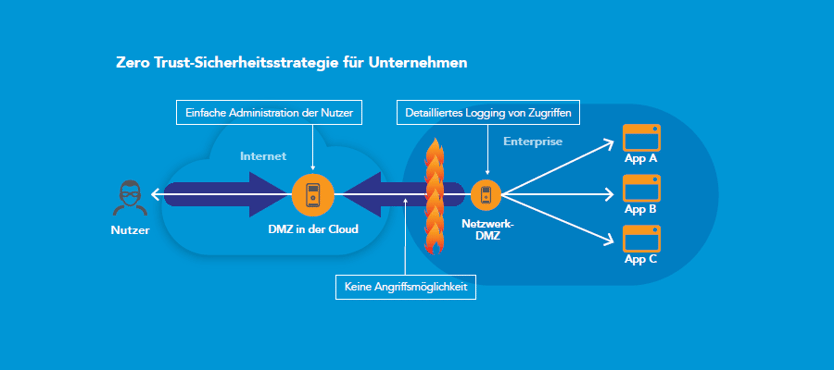 Implement a zero-trust security strategy
Implement a zero-trust security strategy
Zero-Trust isolates applications and the personal data they contain from the internet
Zero-Trust does not differentiate between internal and external network traffic: no one should be blindly trusted, regardless of whether the person is inside or outside your network. As a first step, access to any resource must be explicitly allowed by a central management system and all traffic must be monitored around the clock. The second step is to transform the classic network design based on DMZ into an "isolated services" approach. Access to applications via a DMZ in the cloud thus means that the applications are isolated from the internet and users are kept out of your network. An application and the personal data it contains can only be accessed via the Akamai Intelligent Platform. As a result, Akamai protects your corporate infrastructure and resources, as well as personal data, regardless of whether it is stored in an on-premises or cloud data centre. With this separation and isolation of applications and data, coupled with access logging, you will meet the requirements of audits and data protection impact assessments under the GDPR faster and easier.
Another zero-trust principle says that your employees and their devices are not trusted per se. All activities are monitored and logged. Logging the activities of your employees and service providers will in turn help you to comply with the obligation to provide evidence according to the GDPR.
Since most web attacks use DNS methods, DNS requests from within the company must not only be logged, but DNS must be an integral part of your security strategy as a control point. Here's how that works: As part of a zero-trust approach, the Akamai Cloud DMZ checks all DNS queries. As soon as untrusted links are clicked, e.g. in phishing or ransomware emails, the Cloud DMZ blocks the DNS request and thus protects your users. The Akamai Cloud DMZ protects your business in many ways:
- To deliver applications and data only to "AuthN" and "AuthZ" users and devices.
- To proactively prevent malware and DNS-based "exfiltration everywhere"
The Zero Trust security model follows the motto: Trust no one per se, always check – with full visibility.
Conclusion: The GDPR introduces the concept of accountability, including an obligation to provide evidence for data processing companies. Data processing companies are expected to be fully aware of their processing operations and the corresponding risks to the protection of data. Furthermore, it is required to minimise these risks by taking appropriate measures to safeguard the (data protection) rights and freedoms of natural (EU) persons. Akamai has the world's largest and most advanced cloud delivery platform for the secure distribution and acceleration of web content. Akamai's expertise enables you to better protect the personal data in your web applications from loss and unauthorised access.
By implementing the Akamai Web Application Firewall (WAF), you can demonstrate that you have appropriate measures in place to protect against many known and unknown web threats. The Web Application Firewall combines industry best practices with intelligent, risk-based assessment mechanisms to identify attacks. Fully trained Akamai security experts help your organisation respond to the ever-changing threat landscape. The reports provided can be used to demonstrate that risks of a breach to personal data used in web applications have been anticipated and mitigated by creating and maintaining effective WAF policies. In addition, the risk of multi-vector attacks targeting personal data can be mitigated by implementing a harmonised and integrated DDoS solution at the application level. Finally, Akamai helps customers limit employee and/or supplier access to only the web applications and data they really need, and create audit trails of who accessed which web applications and when. Akamai Services helps customers implement appropriate access controls to personal data in web applications and demonstrate their effectiveness. This minimises the risk of a breach of protection for this data and demonstrates responsible data processing – in line with the GDPR.
Links to the security solutions mentioned in the text:
In addition, we recommend: Akamai GDPR webinar recording (January 2018)
Experts answer – What to consider when processing personal data in web applications
Questions on the topic?
We can advise you together with Akamai on all the solutions mentioned – don't hesitate to contact us.